| (a) |
List four factors to consider when deciding
which network topology to implement. |
[4] |
|
- Expected traffic
- Routing method
- Channel capacity
- Cost
|
|
| (b) |
In circuit switching there is a dedicated
communication pathway between two stations. Briefly describe the three phases involved in
this connection. |
[6] |
|
- Circuit Establishment
Before transmitting a data the end to end must be established. After it is set, test is
used to determine if the end station is busy or is prepared to accept correction.
- Data Transfer
It is generally a full duplex connection. Analog or digital can be transmitted.
- Circuit Disconnects
After finishing data transfer, connection is terminated. Signal must be propagated too
intermediate switching nodes to deallocated the dedicated resources.
|
|
| (c) |
Below is a diagram of a typical network
topology, which assigns routes using the Datagram approach. There are four packets in the
message, which need to be sent from station A to station B. Assume that every packet moves
forward every turn, unless the node or the node in front is busy. The packet is then
stored in the queue and will only move on if the node or the node in front becomes free. 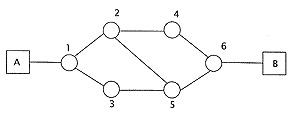
A sequence of events is shown below. Using this sequence,
determine the final arrival order for the packets. Show all working, by indicating the
location of each packet after every step listed below.
1. Packet 1 is sent from station A
2. Nodes 2, 4, 6 are busy
3. Packet 2 is sent from station A
4. Nodes 3, 4, 5, and 6 are busy
5. Packet 3 is sent from station A
6. Nodes 3 and 5 are busy
7. Packet 4 is sent from station A
8. Nodes 3 and 5 are busy
9. Node 4 is busy
10. Node 4 is busy |
[10] |
|
- Packet 1 is sent to node 1
- Packet 2 is sent to node 1, and
packet 1 to node 3
- Packet 3 is sent to node 1, packet 2
is sent to node 2, and packet 1 remains at node 3
- Packet 4 is sent node 1, packet 3 is
sent to node 2, packet 2 is sent to node 4, and packet 1 remains at node 3
- Packet 4 is sent to node 2, packet 3
is sent to node 4, packet 2 is sent to node 6, and packet 1 remains at node 3
- Packet 4 remains at node 2, packet 3
remains at node 4, packet 2 is sent to Station B, and packet 1 is sent to node 5
- Packet 4 remains at node 2, packet 3
remains at node 4, and packet 1 is sent to node 6
- Packet 4 is sent to node 4, packet 3
is sent to node 6, and packet 1 is sent to Station B
- Packet 4 is sent to node 6 and
packet 3 is sent to Station B.
- Packet 4 is sent to Station B
- The final arrival sequence is 2134
|
|
