| (a) | List the four functions of a front-end Processor. | [4] |
|
||
| (b) | Briefly describe the concept of modulation. | [3] |
| Modulation is one of
the technique that modifying the form of electronic signal so that the signal can carry
intelligent information in communication medium. It can either be a analog modulation or
digital modulation.
|
||
| (c) | Explain the following with the aid of diagrams: | |
| (i) Frequency Modulation | [4] | |
| (ii) Statistical Time Division Multiplexing | [4] | |
| (i) Frequency
Modulation is also known as Frequency Shift Keying. The frequency of the sine wave is use
to transmit ones and zeros. The higher frequency is transmit one, the lowest frequency is
transmit zero. It can prevent repeat of transmission. It is a fast modulation commonly use
for radio transmission. (ii) Statistical Time Division Multiplexing is basically similar with Time Division Multiplexing which can transmit of more than one data over the same channel using successive time internal except that STDM dynamically allocates time slot on demands and does not sent any empty time slots. The advantage of using STDM is that STDM can support more subchannel compare with TDM and there is no wasting of time slot. The disadvantage of using STDM is that an additional space is needed for address.
|
||
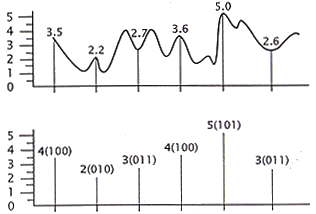
| (d) | Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is one of the most
common digitising techniques in use. The amplitude of each signal is approximated by an
n-bit integer with a digitised modem and the analog wave is then converted. Convert the
analog wave below to its PCM output (i.e. a binary form), using the time points shown as
sampling points.
|
[5] |
PCM output = 0100 0010 0011 0100 0101 0011 |