| 3. |
(a) List two
types of scheduler, and distinguish between them. |
[4] |
|
One
mark should be awarded for each type of scheduler named (up to a maximum of two marks).
Examples include the following: |
|
|
|
Job scheduler;
long-term scheduler |
|
|
|
CPU scheduler;
short-term scheduler |
|
|
A job
scheduler is responsible for admitting jobs, |
[1] |
|
whereas a
CPU scheduler determines the allocation of CPU time to jobs in the ready queue. |
[1] |
|
Similar
answers should also be awarded marks. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) Suppose, in a multiprogramming
environment, a processor is assigned the following jobs for execution. |
|
|
| Job |
Arrival Time |
CPU Time |
Priority |
| 1 |
0 |
7 |
4 |
| 2 |
1 |
5 |
3 |
| 3 |
2 |
6 |
1 |
| 4 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
Priority is highest
for 1 and lowest for 4. |
|
|
|
|
|
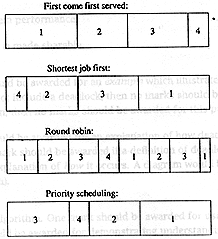
Draw a Gantt Chart to illustrate
the execution of these jobs using the following scheduling algorithms: |
[8] |
|
|
(i) First Come First Served |
|
|
|
(ii) Shortest Job First |
|
|
|
(iii) Round Robin (time quantum is 3) |
|
|
|
(iv) Priority Scheduling |
|
|
Two marks
should be awarded for each Gantt chart which corresponds to those shown below |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(c) For each of the algorithms
mentioned in part (b), compute the average waiting time. You should show all necessary
working. |
[8] |
|
| AWT |
= |
(7 + 12 + 18) / 4 |
|
= |
37 / 4 |
|
= |
9.25 |
|
|
|
| AWT |
= |
(2 + 7 + 13) / 4 |
|
= |
22 / 4 |
|
= |
5.25 |
|
|
|
Waiting
time of J1 = 11 + 5 = 16 |
|
|
Waiting
time of J2 = 3 + 8 = 11 |
|
|
Waiting
time of J3 = 6 + 7 = 13 |
|
|
Waiting
time of J4 = 9 |
|
|
| AWT |
= |
(16 + 11 + 13 + 9) / 4 |
|
= |
49 / 4 |
|
= |
12.25 |
|
|
|
| AWT |
= |
(6 + 8 + 13) / 4 |
|
= |
27 / 4 |
|
= |
6.25 |
|
|
|
Two marks are
available for each part --- full marks should be awarded if the calculation is correct. If
the result is incorrect, then 0.5 marks should be awarded for each correct step. |
|
