| 5. |
(a) Define Artificial
Intelligence. |
[2] |
|
The
branch of computer science which is concerned with the design of systems which exhibit
characteristics of human behavior. Any answer which captures this notion should be award
two marks. |
|
|
|
|
|
(b) Almost all
Artificial Intelligence programs contain problem solving techniques. Describe the three
components of a problem solving technique, and how they relate to one another. |
[8] |
|
One
mark is available for naming each component, and a further mark is available for each
satisfactory elaboration. Two marks are also available for a correct explanation of the
relationship between the entities. Suitable answers are given below: |
|
|
|
The database: this
contains knowledge, which can be stored in different forms. |
|
|
|
A set of operators:
these are used to manipulate data via rules of inference. |
|
|
|
A control strategy:
this determines the next step. |
|
|
|
The relationship
between the entities can be described thus: A set of operators works on a database, |
[1] |
|
|
while a control
strategy makes decisions based on knowledge that is available. |
[1] |
|
|
|
|
|
(c) Describe, with
examples, three ways in which knowledge can be represented in a database. |
[6] |
|
One
mark is available for each correct means of representation (up to a maximum of three
marks). Examples include the following: |
|
|
|
Logic |
|
|
|
Semantic nets. |
|
|
|
Production systems. |
|
|
A further
three marks are available for satisfactory examples. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) Minimax searches
make use of the static evaluation functions to decide its next move. Using the values the
diagram below, decide which is the next best move after A. |
[4] |
|
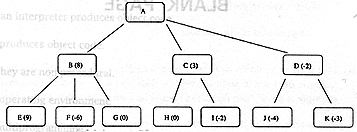
|
|
|
Discuss how you decided on the
next move, specifying in detail the search step motion, the need to use a 2-ply instead of
a 1-ply search, and the ultimate value which prompted you to make the decision. |
|
|
1st
level analysis shows static values of 8, 3, and -2 for nodes B, C, and D respectively. |
|
|
[0.5
marks] |
|
|
2nd level
analysis shows static values of 9, -6, 0, 0, -2, -4 and -3 for nodes E, F, G, H, I, J, and
K respectively. |
|
|
[0.5
marks] |
|
|
If only
level 1 was analysed, the best move would have been B with static value of 8. |
|
|
[0.5
marks] |
|
|
However,
to decide on just this level is short-sighted. |
|
|
[0.5
marks] |
|
|
When
analysing further using the 2-ply search, final values are -6, -2 and -4 for nodes B, C,
and D respectively. |
|
|
[1
mark] |
|
|
The best
move would be C, as it secures the best value of the worst situation. |
|
|
[1
mark] |
|
