| (a) | There haven been attempts to provide a unified approach to cognitive science. However, at this moment, there is no generally accepted concept of what cognitive science is. Briefly describe one problem that may explain this difficulty. | [2] |
| Cognitive science
comprises a diverse range of disciplines, including psychology, linguistics, philosophy
and neuroscience. As a result of the diversity, experts from different fields have
different opinions about what cognitive science is, and therefore, there is no general
consensus on the definition of cognitive science. (If people cannot even agree on what
cognitive science is, then there could be no unified approach!)
|
||
| (b) | Define a predicate expression to define a
triangle using the following predicates : line (A, M,
N) : A is a straight line on a 2 dimensional plane, where M and angle (A, B, D) : Lines A and B have an angle of D degrees. triangle (A, B, C) : Lines A, B and C form a triangle. |
[4] |
| [line(A,P,Q) Ù line(B,Q,R) Ù
line(C,R,P) Ù~angle(A,B,0)] ®triangle(A,B,C)
|
||
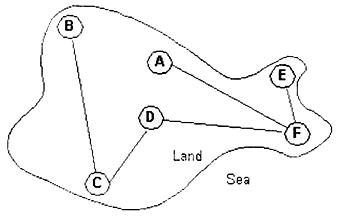
| (c) | The following diagram shows a country where
the major cities are linked by a rail system. You know the distance between the cities. To
get from one city to another, we can proceed without making use of any information about
the geography or the rail system at all, or we can make use of available information
intelligently using heuristics. (i) Briefly describe how you would get from one point to another using the first approach, i.e. a blind approach. (ii) Using only distance as a basis for designing a heuristic approach, explain how you would travel from one city to another. (iii) When would problem solvers employ heuristics?
|
[1] [1] [2] |
| (i) Using a blind
approach, one would simply travel through all the cities linked by the rail system. If the
destination is linked by the rail system, then one would reach the desired destination
eventually.
|
||
| (ii) At the point of
departure, if one of the cities linked to it is the destination, then travel to it. If
none of the linked cities is the destination, then choose a city that will bring you
closer to the destination.
|
||
| (iii) When there were
inherent ambiguities in the problem statement or data (1 mark) and when the problem may
have an exact solution but the computational cost of finding it is too great.
|
||
| (d) | Template matching is one common technique for recognizing patterns. While it had its strengths, template matching has some drawbacks to make it suitable only for some limited applications. Briefly describe two problems of template matching. | [4] |
| Template matching is
inefficient. For each pattern to be matched, a template is needed. Template matching is inflexible. Even if the template for a pattern exists, the size and orientation of the input pattern must be the same as the template.
|
||
| (e) | As natural language is complex, it is broken down into different levels so that it can be managed easily. Briefly describe any six levels. | [6] |
|