| (a) | Describe the basic biology of a neuron. | [3] |
| Answers should include
each of the following: cell body, axon, and dendrites. Where the dendrites of one neutron meet another there is a synapse plus mark for general understanding.
|
||
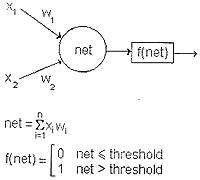
| (b) | A neuron has inputs x1 and x2, and the
corresponding weights w1 and w2. The values of the weights are 0.3 and 0.3 respectively.
The neuron uses a step function and has a threshold of 0.5. (i) Draw a diagram of a neuron, showing the formulae for the calculations (using the figures above) involved in calculating the output. (ii) Given that the inputs are x1=1 and x2=2, and has a target output of 1, calculate the output of this neuron. (iii) Explain how the weight can be adjusted so that the output eventually equals the target. (iv) What other threshold function is used and how does it differ from the step function?
|
[3] [2] [3] [2] |
| (i)
|
||
| (ii) net = x1w1 + x2 w2 = 1 * 0.3 + 0 * 0.3 = 0.3 f(net) = 0 since 0.3 < 0.5
|
||
| (iii) The neutron should fire, but since net < threshold, the weights of the active inputs must be increased so that the net will gradually be greater than the threshold, ensuring that the neuron eventually fires. Since x1 is the only input that has a positive contribution to net, the weight w1 must be increased. |
||
| (iv) Sigmoid (other functions that are suitable can be accepted). It differs because it generates continuous output values.
|
||
| (c) | (i) Name a supervised and an unsupervised
learning algorithm. (ii) Describe supervised learning in neural networks. |
[2] [5] |
| (i) Supervised: back propagation algorithm. Unsupervised: hebbian rule.
|
||
(ii)
|