| (a) |
Explain the terms bit rate and baud .In
what circumstances will they take on different values?
Bit rate
is the number of bits transferred on one second;baud is the number
of signalling elements in one second (1 mark).They will take on different
values if there is more than one bit per signalling element (1 mark).To
gain the marks,candidates must distinguish between the two.Give credit
for valid alternatives.
|
[2] |
| (b) |
What is meant by full-duplex communications?Provide
a suitable example.
Full duplex:transmission
in either direction at any time (1 mark).Plus (1 mark) for a suitable
example.
|
[2] |
| (c) |
With the aid of a diagram,describe frequency
division multiplexing .
In FDM
the total frequency of the communication channel is divided among
a number of users where each user is given a fixed portion of the
frequency spectrum (1 mark).
Some bandwidth between each channel may be allocated to provide a
guard band to provide adequate separation between the frequency allocation
of each channel (1 mark).
Award marks for these or other valid points,plus (1 mark)for a suitable
diagram.
|
[3] |
| (d) |
What are the advantages of using fibre
optics?
immunity
to interference (1 mark),wide bandwidth (1 mark).Award marks for these
or other valid advantages.
|
[2] |
| (e) |
What are the factors that cause attenuation
in fibre optics?
light coupling
(1 mark),splicing (1 mark),light absorbed by glass (1 mark). Award
marks for these or other relevant reasons.
|
[2] |
| (f) |
Why is message switching not suitable
for real-time traffic?
Message switching is subject to delays such as queueing delay (1 mark),and
propagation delay (1 mark);that is,it cannot deliver guaranteed delivery
times (1 mark).Two marks for points from these,or other valid points.
|
[2] |
| (g) |
What is meant by noise in the context
of data communications?Name and describe one type of noise.
Noise is
an undesired signal in the communications circuit (1 mark)which canlimit
a system ’s performance.
Anyone of the following:
thermal noise (1 mark)this arises from electron motion
and is a function of temperature (1 mark).
inter-modulation noise (1 mark)occurs when two signals pass through
a non-linear device (1 mark).
crosstalk (1 mark)occurs when there is electrical coupling between
cables carrying multiple signals (1 mark).
impulse noise (1 mark):irregular pluses of high amplitude that
seriously degrade the data (1 mark).
|
[3] |
| (h) |
Explain one encryption technique,using
an appropriate example.
substitution cipher
(1 mark)—a letter or a group of letters is substituted by another
letter or group of letters (1 mark).Example (1 mark).
or
transposition cipher (1 mark)—the order of letters is changed but
the letters remain unchanged (1 mark).Example (1 mark).
|
[3] |
| (i) |
Name and briefly explain the major elements
of a LAN.
Cabling
systems (1 mark),Protocols (1 mark),Topologies (1 mark), Gateways/Bridges
(1 mark).
For full marks,an explanation is needed;award no more than 2 marks
if no explanation is provided.
|
[4] |
| (j) |
What are the disadvantages of using a
ring topology for a LAN?
susceptible
to a single point of failure (1 mark);complex access mechanism is
needed (1 mark).
|
[2] |
| (k) |
The data-link layer consists of two sub-layers.Name
those layers.
media access
control sub-layer (1 mark);logical link control (1 mark).
|
[2] |
| (l) |
A particular modem is running at
9 600 baud.It modulates signals using both amplitude and phase modulation.The
phase shifts are at 0,90,180,and 270 degrees, with two different amplitude
levels per phase shift.How many bits per second can it transmit?Show
all workings and assumptions you make.
Two amplitudes
and four phases means 8 distinct modulation patterns (1 mark). That
is 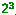 ,so
3 bits may be represented (1 mark).Thus the data rate is 9 600 ×3
=28 800 bits per second (1 mark). ,so
3 bits may be represented (1 mark).Thus the data rate is 9 600 ×3
=28 800 bits per second (1 mark).
|
[3] |