|
Local Area Networks (LANs) are able to deliver
data quickly and reliably over short distances. Various different topologies are
available. |
|
| (a) |
Describe four factors to be considered
in selecting a topology for a LAN. |
[4] |
|
- Physical location
the building or locations where LAN is going to be installed will affect how the topology
contributes.
- Security level
when security is involved, topology of LAN has to be considered carefully. Bus topology
provides broadcast feature hence is not very secured. Star network will be a great choice
for secured network.
- Communication and Control level
if one wants to have a great control of other subnodes, star topology will be a suitable
choice.
- Type of service/usage
when broadcasting is the service, bus will be the topology, for public sharing of devices
(printer, servers), star might be suitable.
|
|
| (b) |
A particular open-plan office is being equipped
with a new LAN. Network sockets are to be arranged in a 3 x 3 grid, as follows: 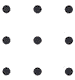
The vertical/horizontal distance between sockets is 4 m; the
diagonal distance is therefore 5.7 m.
What is the minimum length of cable that will be needed if
the LAN is to be |
[6] |
|
(i) a ring, |
|
|
(ii) a bus |
|
|
(iii) a star. State any assumptions you make. You may find it useful to draw a diagram in
each case, showing how the nodes are connected. |
|
|
(i)
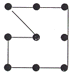
minimum length of cable:
(8*4) + 5.7 = 37.7m(ii)
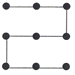
minimum length of cable :
8*4=32
(iii)
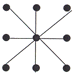
minimum length of cable :
(4*5.7)) + (4*4) = 22.8 + 16 = 38.8m
|
|
| (c) |
What is the IEEE's standard for token passing
ring networks? Describe with the aid of a diagram, the operation of this type of media
access technique. |
[8] |
|
Token ring makes use
of polling technique. 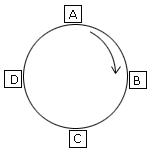
- If A (node) wants to send
information to C, then A has to wait until the token is passed to A (polling).
- A will see whether token is free or
not. If token is free, A will set it into busy token, and append the information to be
sent to the token.
- Token will be passed to B. B ignores
and regenerates the token as the token is not meant for B.
- C receives the token, make a copy of
the frame and information.
- C then set the frame status from 0
to 1, this is to show that C has received the message successfully.
- C then passes the token.
- D receives token and regenerates it.
- A gets back the token , check frame
status for verification of success full transmission, pumps/clears the token and set it
back as free token.
|
|
| (d) |
Which layer of the OSI reference model is
concerned with the specification of cable topologies? Describe one function of this layer
which is independent of the actual medium used. |
[2] |
|
Physical layer
Function : transport transmission of bit (transferring data between the physical medium) |
|




