|
(a) Two architectures of intelligent
systems, the Von Neumann and connectionist architectures, are discussed
in the course material.
(i) Briefly describe the features of the von Neumann architecture
that are
similar to the brain. [3]
(ii) Briefly describe the features of the connectionist architecture
that are
similar to the brain. [3]
(i) When the brain is viewed as a single
unit, it is a central processor
which corresponds to the CPU in von Neumann machines [1].
Knowledge is stored in short and long-term memory depending on
the retention period [1], which correspond to the primary and
secondary storage in von Neumann architecture [1].
(ii) In the connectionist architecture, the brain is not viewed as
a
central processor, but rather as being made up of neurons which
are simple processors working in parallel [1]. Knowledge in
connectionist architecture is stored as connection weights [1],
which simulates the strength of the synapse.[1]
(b) Learning is a permanent change in
knowledge and behaviour that comes as a result of experience. Briefly
describe classical conditioning and observational
learning. From young, we were trained to vacate a building if the
fire alarm
rings. What type of learning is involved? [3]
(i) Classical conditioning involves the association
of a conditioned
stimulus with a conditioned response [1]
(ii) Observational learning is learning from watching others, and
not
from direct experience. [1]
(iii) Operant conditioning [1]
(c) Sorting is a task that is often
performed by us in daily life as well as in automated processes. For
each
(i) Throw away the mackerals and keep everything else [1]
(ii) Put the blue fish in bin 1 and the red fish in bin 2. [1]
(i) identification [1]
(ii) discrimination [1]
(d) “Heuristic search allow us
to find the best path to the goal-state”. Explain why this statement
is false. [2]
Heuristic search uses knowledge of the problem
to choose a path that
has the highest likelihood of leading to the solution [1]. As it does
not
traverse the entire problem space, it is not guaranteed that the path
found is the best path.[1]
(e) Fuzzy logic extends binary logic
to handle certain situations that are not
possible for binary logic to handle.
(i) How do the two types of logic differ with respect to the result
generated? [1]
(ii) Briefly describe the term ‘linguistic variable’, giving
an appropriate
example. [2]
(iii) Let 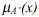 represent
the membership value of the output fuzzy set after a represent
the membership value of the output fuzzy set after a
fuzzy operation on the fuzzy set A with a value of x in the universe
of
discourse. State the operation that is performed by the formula
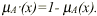 .
If A is the fuzzy set tall, what is the fuzzy set A’? [2] .
If A is the fuzzy set tall, what is the fuzzy set A’? [2]
(i) The output of binary logic can be 0 or
1 only, while the result of
fuzzy logic is in the range of 0 to 1. [1]
(ii) A linguistic variable is a term in natural languages that are
vague
or fuzzy in meaning [1]. An example is ‘tall’. [1]
(iii) Complement operation [1]. A’ is the ‘not tall’
or ‘short’ set. [1]
(Technically, ‘tall’ complement may not be ‘short’
– it may be a
combination of ‘short’ and ‘medium height’ set.)
(f) Edge detection is an activity in
low level vision.
(i) What are edges in an image? [1]
(ii) Why is edge detection important? [1]
(i) An edge in an image occurs when there
is a significant change in
light intensity between adjacent pixels. [1]
(ii) Edges in an image generally correspond to object boundaries.
[1]
(g) Briefly describe feature analysis
with respect to visual pattern recognition. [2]
Objects are composed of distinctive and separable
parts known as
features. [1] Pattern recognition is achieved by comparing entries
in a
database.[1]
(h) The Turing test has often been criticised
for being biased towards symbolic
solving tasks as well as making the assumption that only human beings
are
intelligent enough to be used as basis for comparison. Briefly describe
two
other weaknesses of the test. [4]
The test emphasizes computational language
processing too much. [1]
While one feature that contribute to intelligence is linguistic ability,
other important features are either evaluated in passing, or not evaluated
at all in the test. [1]
In human being, the faster and more accurately a person solve a problem,
the more intelligent he is considered to be.[1] However, in the test,
if the computer performs computation faster and more accurately or
consistently than a human being, the interrogator would be able to
detect that it is a machine. [1]
(i) In the context of Natural Language
Processing, define the following terms: [4]
(i) syntax
(ii) semantics
(iii) pragmatics
(iv) world knowledge
(i) the rules for combining words into legal
phrases and sentences [1]
(ii) the meanings of words, phrases and sentences [1]
(iii) the ways language is used and its effects on the listener [1]
(iv) knowledge of the physical world, the world of social interaction:
background knowledge that is essential to understand the
meaning of a text or conversation [1]
|