|
(a) What are the major functions of a
CPU? [1]
(b) For these two assembly instructions:
LOAD AX, 10
MUL 10, 10, [10]
(i) State the instruction format clearly indicating the Opcode and
the Operand. [2]
(ii) Write the steps of the execute-cycle for each of the above instructions.
[5]
(c) The following sequence of opcode instructions has been produced
to use a stack to evaluate an expression.
PUSH 10
PUSH 10
PUSH 2
PUSH 2
MUL
ADD
PUSH 3
PUSH 3
ADD
ADD
SUB
POP A
(i) What is the expression being evaluated? [1]
(ii) What is the final result of the evaluated expression? [1]
(iii) What is the required stack depth to evaluate this expression?
[1]
(iv) Rewrite the above sequence of instructions to compute the same
expression,
using a 3-address instruction format. [3]
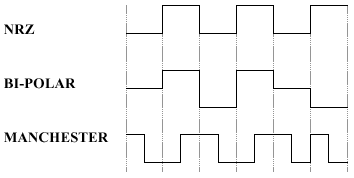
(d) Identify the Bit-stream encoded on
each of the following digital signatures: [3]
(e) Considering what happens when a program
is running, what is the main difference between main memory and secondary-memory?
[2]
(f) What is the characteristic that determines the difference in the
time taken to retrieve data using a Random-access method, when compared
to a Direct-access method? [2]
(g) A typical computer system displays several layers of memory, based
on the diagram below:
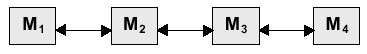
(i) Identify the different levels of
memory, assuming that M1 is the fastest form of
memory. [2]
(ii) Identify the unit of transfer between the memory categories.
[2]
(h) Many of today's organisations’ large LAN topologies such
as Bus, Star, Tree, etc. are no longer single architectures. Rather,
many of these topologies are multi-configurational, meaning that they
combine two network topologies together as one. One such combination
is Bus/Star.
(i) Illustrate what such a network would look like. [1]
(ii) Describe two advantages and two disadvantages of this network.
[4]
|

