|
(a) The time taken by a
milkman to deliver milk to the High Street is normally
distributed with mean time 12 minutes and standard deviation 2 minutes.
Work
to 4 decimal places in this question.
(i) Calculate the probability that, on a given day, he takes less
than 13
minutes to deliver the milk. [3]
(i) Transform to standard normal variable
Z:
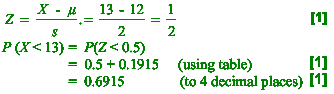
(ii) Calculate the probability that, on a given day, he takes more
than 9
minutes to deliver the milk. [3]
(ii) Transform to standard normal variable
Z:
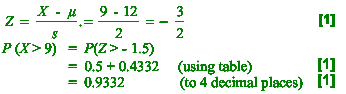
(iii) Calculate the probability that, on a given day, he takes between
9
minutes and 13 minutes to deliver the milk. [2]
(iii)
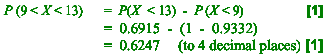
(b) Let A, B and C be sets.
Draw a Venn diagram of the following sets.
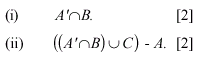
(i) 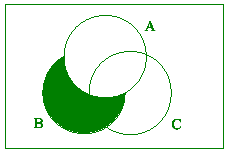 [2] [2]
(ii)
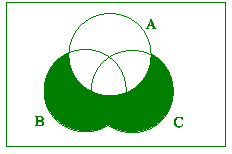 [2] [2]
(c) Give 2 advantages and
2 disadvantages of simulation. [4]
Advantages of simulation:
- Simulation can provide solutions when analytical techniques are
not
available.
- The models to be simulated can represent a real-world process more
realistically because fewer restrictive assumptions are required.
- For instance, random arrivals in a queuing model need not follow
a
Poisson distribution.
- Simulation is less costly than actual experimentation.
- Simulation is a very flexible technique which can be applied to
a wide
vareity of situations.
- Simulation allows for time-compression.
Any two from this list. [2]
Disadvantages of simulation:
- Simulation does not produce an optimum solution, it merely indicates
an approximate behaviour for a given set of inputs.
- Although all models are simplifications of reality, model-building
may
still be complex and time-consuming.
- Practical simulation involves use of computers which may be a
handicap to firms without computer facilities.
- Monte Carlo simulation is application only in situations which have
random elements.
Any two from this list. [2]
(d) A three-year investment
is being considered for which the net cash flows have
been estimated as follows:
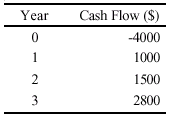
Give your answers correct to 3 significant figures in this question.
(i) Calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) of the project when the
cost of
capital is 10%. [3]
(i)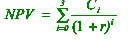
The Ci are the cash flows given in the table, and r = 0.1, so NPV
= $252 (to 3 significant figures). [3]
(ii) Calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) of the project when the
cost of
capital is 15%. [3]
(ii) This time, r = 0.15, and so NPV = -
$155 (to 3 significant figures). [3]
(iii) Use linear interpolation and your answers to parts (i) and (ii)
to calculate
the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) for the project. [3]
(iii) By linear interpolation,
IRR = 10% + 5% (252/(252 + 155))
= 13.1% (to 3 significant figures) [3]
(e) One conventional die
has faces numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Another die has faces numbered
4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6. The score for a throw is the number on the face
which is uppermost when the die is thrown on a horizontal table. If
these two dice are thrown, calculate the probability that the total
score on the two dice is greater
than or equal to 10. [5]
(e) 12 ways in which a score greater than or equal to 10 can be thrown:
(4,6), (4,6), (5,5), (5,5), (5,6), (5,6), (6,4), (6,4), (6,5), (6,5),
(6,6), (6,6). [3]
The two dice can be thrown in 36 ways. [1]
So probability that the total score is greater than or equal to 10
is
12/36 = 1/3 [1]
|
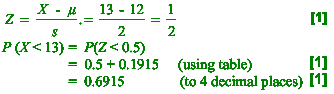
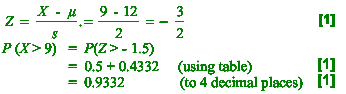
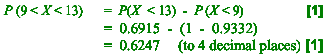
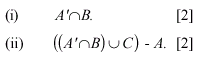
 [2]
[2] [2]
[2]