|
(a) What is float? Explain
briefly the difference between any two types of floats
that you know. How could you calculate each of them? [5]
(a) Float is spare time. [1]
Only two of the following are required:
- definition of total float, TF = LFT - EST - D
- definition of free float, FF = EFT - EST - D
- definition of independent float, IF = EFT - LST - D
[any two of the above,[2]marks each]
(b) Competition is very
great in the personal computer market. The Green
Company is considering whether or not to conduct a market survey to
analyze
the potential sales of their new design, PX-20. This would cost $0.25
million.
The outcome of the survey would either be favorable or unfavorable.
Based on
past experience, the probability of favorable outcome is 0.61.
If they decide not to enter the market, they can sell their patents
for the product
for $1 million; if they decide to enter the market, they will go into
large-scale
production of the PX-20. They have also developed the probabilities
and the
expected profit figures under different conditions:
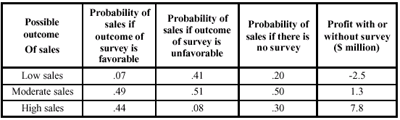
Develop the decision tree and determine whether or not the survey
should be
taken. Recommend a course of action based on the EMV criterion. Comment
on one limitation of this method of analysis. [10]
(b) Drawing [4]; Analysis [5];
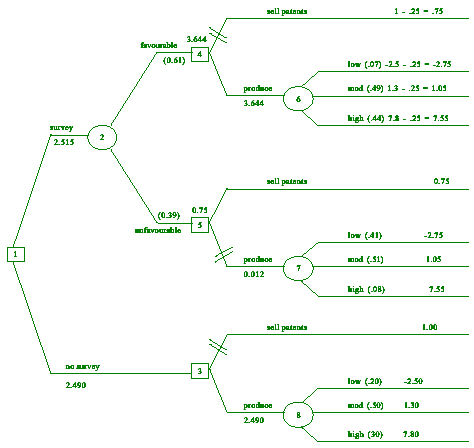
The optimum
course of action is to conduct the survey. If the survey
result is favorable, the product should be produced. If the survey
is
unfavorable, the product should not be produced and the patents should
be sold.1 practical limitation expected. [1]
|

