|
(a) What are the objectives of defining
the requirements of a new system? [2]
- To assemble the overall picture of inputs,
outputs, operations and
resources required by the system to meet the present and future
needs of the organization. [1 mark]
- To determine the criteria that can be used to evaluate the new system
performance. [1 mark]
1 marks each for a clear explanation of each point up to 2 mark.
(b) Compare a Static System against a Dynamic System. [2]
- Static = Never change. [1 mark]
- Dynamic = Continually changing. [1 mark]
1 marks each for a clear explanation of each point up to 2 marks.
(c) Why would a more experienced analyst be more efficient than a
junior analyst
in Requirement Determination? [2]
- Able to see areas otherwise overlooked.
[1 mark]
- Problems or new features that are required can be anticipated. [1
mark]
1 marks each for a clear explanation of each point up to 2 marks.
(d) Capacity is the ability of the system of people, equipment, space
and procedures to achieve the basic objectives and purpose of the
system. The three general strategies of meeting the capacity requirement
are increase capabilities, lower expectations and redefine nature
of task. Give examples of each of these
strategies. [3]
- Get a new Server to meet user expectation
of service.
- Explain that it is impossible to produce 100,000 items in a day
due to
budget or time or manpower constraints.
- Eliminate the need for keying in price and item code at the casher
point with a automatic bar-code reader which saves the information
of the transaction to disk.
Any suitable example may be accepted. 1 marks each. However please
note that only credible IT related example deserve the mark.
(e) Describe three strategies to consider
when dealing with system controls from a system design viewpoint.
[6]
- Design to avoid control lapses. [1 mark]
- Detect and report control lapses [1 mark]
- Detect and fix control lapses [1 mark]
1 mark should be awarded for naming a strategy and one mark should
be
awarded for a satisfactory elaboration.
(f) The advantages of prototyping are: user orientation, fast development
time,
fewer errors and more opportunity for changes. Describe each of these
advantages. [4]
- User Orientation – One major objective
of prototyping is to develop
systems that meet user needs to a greater extent. [1 mark]
- Fast Development Time – Prototyping is fast in obtaining a
working
model whereas structured approached would have taken years. [1 mark]
- Fewer Errors – Prototyping allows early error detection. [1
mark]
- More opportunity for change – User can see the work. They can
as a
result able to propose changes. [1 mark]
1 marks each for a clear explanation of each point.
(g) ABC Bank has just finished an in-house development for their banking
system.
There was a need for this software because the old software was running
on the
legacy system, which was becoming too expensive to maintain. Which
Implementation technique would you recommend? Justify your answer.
[3]
- Parallel run. [1 mark]
- Justification. – Effectiveness may affect the business. Therefore
old
system serves a backup when the new system fails [1 mark]
- The old system may serve as a system to check correctness of the
new system [1 mark]
1 mark each for a clear explanation of each point.
(h) What are Future Requirements? Explain why is it important to anticipate
such
requirements. [2]
- Requirements that will cater for future
growth. [1 mark]
- Avoid need for maintenance in the future. [1 mark]
(i) Bank Brent is a consumer bank. Every month end, the bank will
run a closing
program to generate statements of loan status to its clients. In the
outstanding
loan module, the system will compute the amount due in the month.
If the
previous month’s payment is not made, a nominal 3% interest will
be charged.
All information is updated in the database and printed. This process
is repeated
for all outstanding loans. Draw a structure chart to illustrate this
logic. [6]
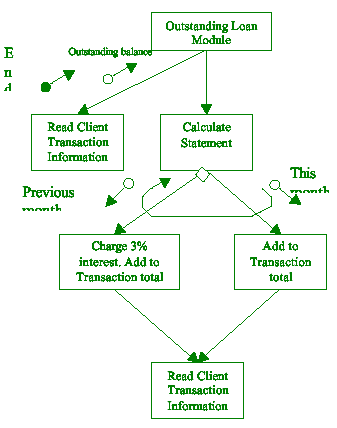
1
mark for one correctly identified process (up to 4)
1 mark for selection
1 mark for control information
student may present variations of the chart.
|
