| (a) |
Threats to system security can threaten
confidentiality, integrity and availability.
Threats
to system security:
(i) Distinguish between these three categories
of threat. [3 marks]
Confidentiality
refers to those services required to protect information from unauthorized
disclosure;
integrity refers to those services required to ensure that information
is accurate, complete and authentic;
availability refers to keeping the system’s hardware and software
working efficiently.
(1 mark each.)
(ii) Which category covers looking over
the shoulder of the person at the terminal
next to you and reading information on their screen? [1 mark]
Confidentiality.
(iii) Which category covers an attack
which swamps a network with millions of copies of the same email message?
[1 mark]
Availability.
(iv) Which category covers a program
that masquerades as a login screen, collecting user passwords? [1
mark]
Confidentiality.
(v) Which category covers breaking in
to a college administration computer and changing your academic record?
[1 mark]
Integrity.
|
[7] |
| (b) |
Trojan horses, viruses and worms are
three means of attacking computers by software.
(i) Give
an example of each means. [3 marks]
Examples:Trojan
horses, viruses and worms
Trojan horse: for example, masquerading as a normal compiler, but
producing bogus object code which performs arbitrary actions with
the user’s authority;
Virus: for example, the Melissa virus, which spreads by sending itself
as an attachment to email from Microsoft Outlook;
Worm: for example, Robert Morris’ Internet Worm, which brought the
Internet to a standstill in 1988.
(1 mark each; of course, there are many reasonable examples.)
(ii) What distinguishes trojan horses
from viruses and worms? [1 mark]
Trojan
horses do not replicate, whereas viruses and worms do.
(iii) What distinguishes a virus from
a worm?[1 mark]
A worm
is a standalone program, whereas a virus is attached to another program.
(Or:) A worm replicates by itself, whereas a virus requires its host
program to execute in order to replicate.
|
[5] |
| (c) |
The RSA public-key cryptosystem uses
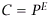 mod
N for encryption, and mod
N for encryption, and 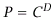 mod
N for decryption. Which of E, D and N should be made public and which
kept secret, and why? mod
N for decryption. Which of E, D and N should be made public and which
kept secret, and why?
Components
of RSA algorithm:
• E is used for encryption, so needs to be public;
• N is the modulus, and is also needed for encryption, so should also
be public;
• D is used for decryption, so should be secret.
(1markeach;no explanation,no mark.)
|
[3] |
| (d) |
Explain the similarities between
written and digital signatures.
Any three
of the following:
Signature is not reusable: signature is a function of the document,
so cannot be transferred to another document;
Signature is unforgeable: only the sender knows the private key (Study
Guide says ‘unforgettable’ here, which makes little sense — but it
should receive credit);
Signature is authentic: receiver verifies the message using the sender’s
public key;
Signature cannot be repudiated: receiver does not need sender’s help
or cooperation to verify signature;
Signature is unalterable: if the signature is altered, it can no longer
be verified.
(1 mark each, to a maximum of 3 marks; no explanation, no mark.)
|
[5] |
| (e) |
Identify and give an example of
three classes of means of proving one’s identity to an authentication
system.
Means of
proving identity: Something you know: eg, a password;
Something you
have: eg, keys, tokens, badges and smartcards (any one will do);
Something you
are: biometric characteristics, eg, a fingerprint or retinal pattern.
(1 mark each;
no example, no mark.)
|
[3] |
| (f) |
What is meant by the term biometrics?
State the most and the least secure biometric devices in use.
Biometrics
is the use of unique physical, behavioural and morphological characteristics
to provide positive personal identification (1 mark). The
most secure biometric characteristic is the retina pattern (1 mark);
the least secure is the signature(1 mark)
|
[3] |
| (g) |
What is the main objective of disaster
recovery? Explain the different approaches used to achieve this objective.
Disaster
recovery aims to minimize the impact of a disaster (1 mark),andtoenjoya
speedy and accurate recovery to normal operation (1 mark). Two approaches:
Avoid it: protect computer equipment and data against all anticipated
risks;
If you cannot
avoid it, reduce it: try to control the damage, should a disaster
happen.
(1 mark each;no
explanation,no mark.)
|
[4] |