| (a) | What information, as opposed to data, in the context of information management? Identify two properties of information, and explain the difference (with respect to these properties) between information suitable for operational control and information suitable for strategic planning. | [6] |
|
||
| (b) | Outline two reasons for an organization to provide continuous training for its staff. | [2] |
The two reasons are:
|
||
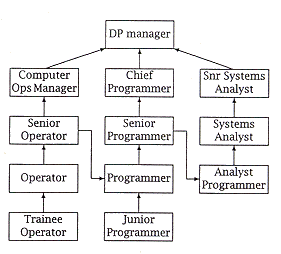
| (c) | Give an example, with the aid of a diagram, of a career ladder for a small data processing department. | [4] |
|
||
| (d) | Explain the difference between theoretical and physical benchmarking of hardware proposals. Why are two separate benchmarking processes used? | [2] |
| Theoretical
benchmarking To verify the specifications solely claimed by the vendor in the request for proposal report. Physical
benchmarking Theoretical benchmarking could eliminate the number of products used to be tested in the physical benchmarking.
|
||
| (e) | Explain what is meant by the term separation of EDP functions; in particular, what is the purpose of this separation? Give two guidelines for achieving this separation. | [4] |
| Separation of EDP
function is a method of general controls employed to the organisation as to limit the rate
of involvement of the employees in a particular information in order to eliminate frauds
and sabotage being committed. Two guidelines:
|
||
| (f) | What is a firewall? | [2] |
| Firewall is a mechanism to protect the network from unauthorised access to the organisation communication network from remote side and other network systems. |