| 1. |
(a) What are the duties of a typical project
manager?
|
[4] |
|
The
duties of a typical project manager:
- working with the steering committee to achieve the project
objectives
- maintaining communication with the users
- planning the project
- staffing the project
- monitoring and reporting upon progress
- adapting and adjusting for changes
one mark for each point given, up to a maximum of four for
this part of the question
|
|
|
(b) List and explain two different
types of maintenance.
|
[4] |
|
The
different types of maintenance:
- corrective maintenance: correcting errors and
problems once they have occurred
- adaptive maintenance: changing system in response
to changes in requirements or methods
- perfective maintenance: changing a working system
to improve performance or efficiency
- preventative maintenance: inspection and review of
the system to detect errors or anticipate potential problems
for each of any two answers, one mark for the type, one mark
for the explanation
|
|
|
(c) Copy and complete the following diagram to
identify the different steps in the risk control cycle: 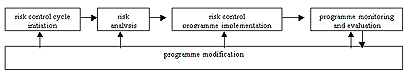
Briefly explain each of the steps you that you have identified.
|
[4] |
|
- risk analysis: identification,
assessment and selection of risks (1 mark)
|
|
|
- risk control programme
implementation: measures are taken for risks of high severity or vulnerability (1 mark)
|
|
|
- programme monitoring and evaluation:
programme is monitored to ensure that risks have been properly analysed and that measures
have been effective (1 mark)
|
|
|
- programme modification: weaknesses
that have been identified may need to be corrected; new threats may be identified (1 mark)
one mark for each stage identified provided
that it is properly explained: no proper explanation = no mark
|
|
|
(d) In auditing a computer system, we may
decide to audit around the computer, or to audit through the computer. Compare and
contrast these two approaches.
|
[4] |
|
- auditing around: examine input and output only (1 mark),
suitable if the system logic is straightforward (1 mark), or the environment is constant
(1 mark), or there is a clear audit trail (1 mark). Also suitable if well-known package (1
mark), and has the advantage of simplicity (1 mark). one mark for each point,
to a maximum of two marks
|
|
|
- auditing through: examine logic within the system itself
(1 mark), more expensive (1 mark), suitable if predicting response to change is important
(1 mark), needed if logic is complex (1 mark), high volume of I/O (1 mark), system is
mission critical (1 mark), or there are substantial gaps in the audit trail (1 mark) one
mark for each point, to a maximum of two marks
up to two marks for each approach
|
|
|
(e) In your own words, suggest at least two
ways in which the turnover rate of staff may be related to the difficulty of
recruiting qualified personnel.
|
[4] |
|
The relationships
between turnover rate of staff and the difficulty of recruiting qualified personnel:
|
|
|
- high turnover puts pressure on those
involved in the recruiting process, as new recruits are always needed
|
[1] |
|
- a lack of suitable recruits may mean
that existing staff are forced to work under pressure, and may leave sooner, increasing
staff turnover
|
[2] |
|
- high turnover in the industry as a
whole may mean that it is easier to recruit qualified personnel; more staff are moving
between jobs, and are thus available to be recruited
|
[2] |
|
- high turnover may mean that qualified people are in short
supply in the industry as a whole, and that they are being head-hunted; in this case,
recruitment will be difficult
the question asks for an explanation in the candidate’s
own words; the marks above suggest a manner in which these answers might be assessed
– the first point is relatively simple, the others are more subtle and indicate more
thought. To a maximum of four marks. |
[2] |